Treatments Options for UTI
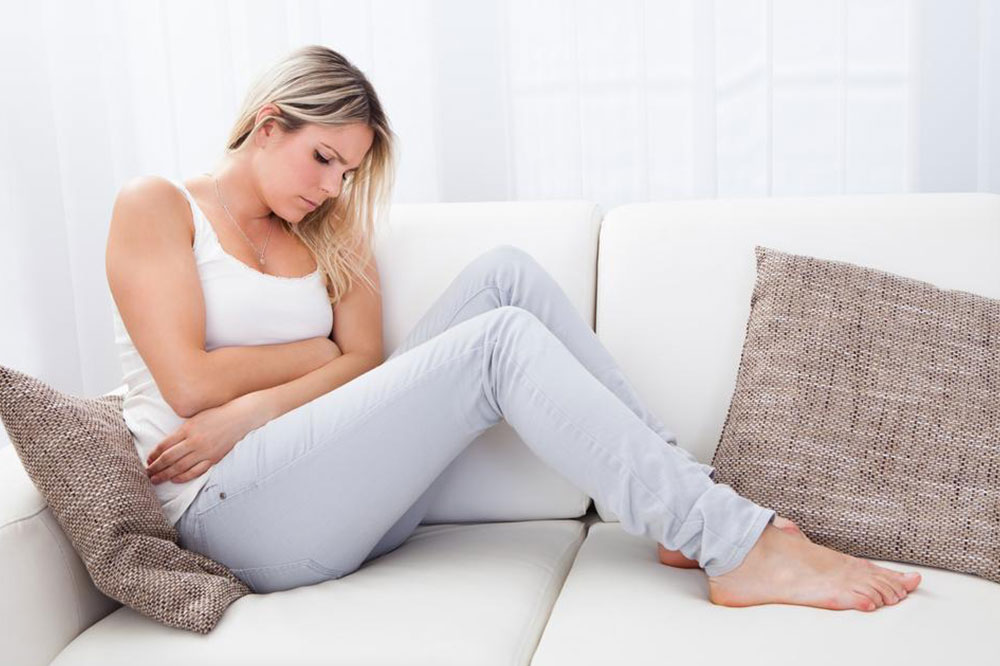
Every year, urinary tract infections (UTIs) affect over six million people in the country. Fortunately, there are several treatments for UTIs. The doctor will apply different treatment methods depending on the type of UTI you have and your health conditions. Usually, antibiotics are the first line of treatment for UTI. You can find the most common approaches to treating UTI below.
Medications
If you have a simple infection, the doctor may prescribe commonly used antibiotic medicines. They include trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, fosfomycin, ceftriaxone, and cephalexin. The course for an uncomplicated UTI lasts for just one to three days. If your symptoms persist, the doctor might advise you to continue the medications for a week and sometimes more. Although you may find relief from pain soon after starting an antibiotic course, you should finish the prescribed course to ensure that the treatment does not remain incomplete. UTIs can often return if the treatment procedure is unfinished. Doctors, however, refrain from prescribing fluoroquinolones(ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin) for treating the simple infection as the risk outweigh the benefits of treatment.
Topical Treatment
For UTI in postmenopausal women, the doctor may suggest a topical treatment. In this treatment method, estrogen is used for hormone replacement because it encourages the production of natural antimicrobial substances in the bladder. Moreover, this treatment method strengthens the urinary tract tissue, making it difficult for bacteria to penetrate the bladder wall.
Your doctor may recommend specific treatments for UTI if it occurs frequently. Prescription lose-dose antibiotics for six months can treat your UTI sometimes. It can also prolong. If your UTI is related to sexual activity, you may be advised to use a single dose of antibiotics after intercourse.
Oral or Intravenous Antibiotics Course
While most women are diagnosed with an uncomplicated UTI, men, and children most often suffer from complicated infection. For this type of UTI, the prescription course of antibiotics goes on for a more extended period. Depending on the severity, you may need to start your treatment intravenously (IV) in the hospital. After you are treated intravenously for a short period, the doctor may put you on oral antibiotics for up to two weeks. Kidney infection also falls under complicated UTI and is treated accordingly.
Painkillers
For managing your symptoms of burning sensation while urinating, the doctor may also prescribe analgesic or pain medication. The analgesic numbs your bladder and urethra so that there is no burning pain during urination.
The treatment of UTI generally consists of these methods mentioned above. Unless your UTI occurs due to an anatomical problem, it is improbable that you will need surgical treatment. Sometimes a blockage like an enlarged prostate or kidney stone can become the cause of UTI. You might need an operation in these cases. While these methods are standard, research also supports some natural remedies like staying hydrated, getting enough vitamin C, and urinating when the need arises.